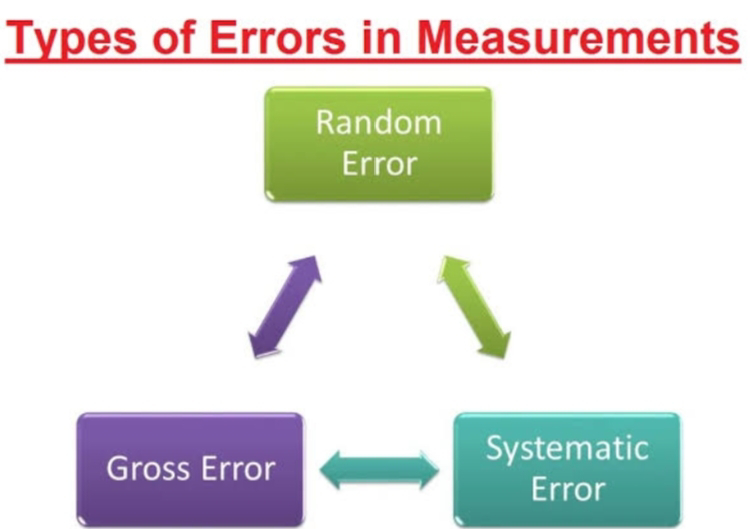
sampling , sample preparation , analysis , interpretation , preparation of report and pipette , burette , chemical balance and least count ( for B.A. , B.Com. and B.Sc. ) analytical chemistry unit 3 and 4

- Steps in chemical analysis - You've outlined the key steps in chemical analysis correctly. Here's a bit more detail on each of those steps: You've outlined the key steps in chemical analysis correctly. Here's a bit more detail on each of those steps: 1. Sampling: - This is the process of selecting a representative portion of the material or substance to be analyzed. The accuracy of the analysis depends on the quality of the sample, so it's essential to collect it carefully. 2. Sample Preparation:- Once the sample is collected, it often needs to be prepared. This could involve grinding, filtering, diluting, or any other steps necessary to make it suitable for the specific analysis method. 3. Analysis:- In this step, you perform the actual chemical analysis. This can involve various techniques, such as spectroscopy, chromatography, titration, or any other method relevant to the specific analysis goal...